#apixaban intermediates
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Apixaban API manufacturers
Apixaban API manufacturers Actis. Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients, Intermediates to our wide range of customers. By ensuring high purity and quality

0 notes
Text
Top Demand Drug companies in India in the Last Decade

Over the past decade, the demand for drug companies in India has significantly increased, reflecting the country's evolving healthcare industry. In fact, a report by Statista indicates that the Indian healthcare and pharmaceuticals sector is anticipated to experience an extraordinary growth rate of 754% between 2017 and 2060.
As India emerges as a major player in the pharmaceutical industry, it is critical to understand the demand for various drugs in the country. It provides valuable insights into the health concerns of the people, the shifting demographics, and the evolving medical requirements.
So, read the article below to gain in-depth knowledge about high-demand drugs in India and the factors influencing this demand. This knowledge can help drug companies to focus their R&D and production to cater to the specific needs of the Indian market.
Top 8 Demand Drugs in India
Some of the best drugs in India and their uses are given below:
1. Humira
Humira (adalimumab) is a widely used biological medication known for its effectiveness in treating various conditions. It functions as a tumor necrosis blocker, which helps suppress the immune system by blocking the activity of factor-α (TNF). TNF is a protein associated with inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
Uses
Treats rheumatoid arthritis in adults.
Indicated for adults with hidradenitis suppurativa (HS).
Tackles chronic plaque psoriasis.
Treats non-infectious intermediate, posterior, and panuveitis.
Approved for adult patients with active ulcerative colitis.
Used to reduce signs and symptoms of active ankylosing spondylitis.
2. Keytruda
Keytruda is a cancer medication that contains the active substance pembrolizumab. It belongs to a class of drugs known as immune checkpoint inhibitors. Keytruda blocks a protein called PD-1 in immune cells. This allows the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
Uses
Treats advanced or metastatic melanoma.
Treats advanced NSCLC.
Treats children with classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
Treats advanced renal cell carcinoma.
Used in combination with chemotherapy or other cancer medicines to treat oesophageal cancer.
Prevents blood clots in cases like broken bones, immobility, surgeries, etc.
3. Eliquis
Eliquis is a prescription medication that belongs to the class of drugs known as anticoagulants or blood thinners. It is considered an anticoagulant because apixaban is its active ingredient. Eliquis is FDA-approved for treating and preventing dangerous blood clots that can block blood vessels in the body.
Uses
Treats deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Prevents stroke.
Treats pulmonary embolism (PE).
Reduces the risk of systemic embolism.
Avoids thromboembolic events in individuals with chronic kidney disease.
Used as an anticoagulant therapy during cardiac catheterization procedures
4. Revlimid
Revlimid is a medication that contains the drug lenalidomide. It is a thalidomide analog, an immunomodulatory drug (IMiD) with various putative molecular targets and biological effects. Revlimid is primarily used to treat multiple types of cancers affecting blood cells.
Uses
Used in combination with dexamethasone for the treatment of multiple myeloma.
Used as maintenance therapy after an autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant (auto-HSCT).
Treats lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma.
Used off-label for the treatment of systemic light-chain amyloidosis.
Tackles myelodysplastic syndromes.
Used in combination with rituximab to treat follicular and marginal zone lymphoma.
5. Imbruvica
Imbruvica is a medication available in tablet and capsule forms that are taken orally once a day. Its active ingredient is ibrutinib. Ibrutinib works by inhibiting specific proteins in cancer cells, slowing their growth, and preventing the spread of cancer.
Uses
Treats mantel cell lymphoma (MCL).
Treats chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Tackles small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL).
Treats waldenström's macroglobulinemia (WM).
Manages chronic graft versus host disease (cGVHD).
Prescribed off-label to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
6. Stelara
Stelara is a highly effective medication that contains ustekinumab. Ustekinumab is a monoclonal antibody derived from immune system cells. It is specifically designed to target and alleviate the symptoms of various inflammatory conditions associated with immune system dysfunction.
Uses
Provides relief for people suffering from this autoimmune skin condition.
Treats psoriatic arthritis for adults.
Deals with the challenges of moderate to severe Crohn's disease.
Treats adults with this type of inflammatory bowel disease.
Used off-label in the treatment of active systemic lupus erythematosus.
Used for investigational purposes of hidradenitis suppurativa.
7. Xarelto
Xarelto (rivaroxaban) is a medication also classified as a blood thinner. It works by inhibiting the activity of Factor Xa, an enzyme involved in blood clot formation. While Xarelto does not thin the blood, it helps prevent the formation of blood clots and reduces the risk of strokes and systemic embolisms in certain medical conditions.
Uses
Reduces the risk of stroke and systemic embolism with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation.
Treats and maintains drugs for deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
Reduces the risk of recurrence of pulmonary embolism.
Prevents blood clot formation in patients suffering from heart failure, respiratory disease, or infectious diseases.
Used as a prophylactic treatment to prevent blood clots in patients with cancer.
Prevents the recurrence of ischemic events, such as heart attacks or peripheral artery disease
8. Opdivo
Opdivo is an immunotherapy drug that belongs to a class of medications known as checkpoint inhibitors. It targets the PD-1 receptor, found on the surface of T cells, the immune cells responsible for fighting cancer. PD-1 helps regulate immune responses in healthy tissues, but cancer cells can exploit this mechanism to evade immune attacks. Opdivo blocks the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1/PD-L2 molecules in cancer cells. This blockage enables T cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells effectively.
Uses
Treats advanced melanoma.
Treats non-small cell lung cancer.
Used in combination with ipilimumab for newly diagnosed malignant pleural mesothelioma.
Treats adult patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
Treats patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Treats with microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair-deficient (dMMR) metastatic colon.
Factors that Impact the Demand for the Drugs
Here are four key factors that impact the demand for drugs:
1. Disease Prevalence and Epidemiology
The prevalence of diseases and their impact on the population greatly influence the demand for drugs. The burden of chronic diseases, or infectious outbreaks, shapes the market for specific medications to treat and manage these conditions.
2. Demographic Changes
Changing demographics, such as aging populations and urbanization, play a crucial role in drug demand. Different age groups have varying healthcare needs, and understanding demographic shifts helps target drug development and delivery strategies accordingly.
3. Economic Factors
Economic factors, including income levels, affordability, and healthcare expenditures, substantially impact drug demand. If medicines are expensive or not affordable, people may struggle to access their prescribed treatments. The cost and accessibility of medications greatly affect the choices people make and their ability to follow through with the necessary treatments.
4. Government Policies and Regulations
Regulatory frameworks, pricing regulations, reimbursement policies, and intellectual property rights all affect the availability, accessibility, and affordability of medicines. This further influences its demand in the market. Understanding and navigating these factors is crucial for ensuring that drugs are accessible and affordable to those who need them.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, understanding the demand for drugs in India is vital for pharmaceutical companies, policymakers, and healthcare providers. By now, you must be aware of the factors that significantly impact drug demand. By aligning their strategies with these factors, stakeholders can meet the evolving healthcare needs of the Indian market effectively.
Moreover, if you're looking for a trusted name in the pharmaceutical industry for reliable and high-quality medications, consider Mediwin Pharmaceuticals. They have been one of the top pharma companies serving India since 1990. It is among the top pharmaceutical manufacturing companies in Ahmedabad because they facilitate effective medications for chronic conditions, specialized therapies, and preventive care.
So, visit Mediwin’s website today to discover its diverse product portfolio!
Source link
#drug companies#pharma manufacturing companies in ahmedabad#pharma industry in ahmedabad#top pharmaceutical companies#pharma industry#top pharma companies
0 notes
Text
Apixaban API Manufacturers

Apixaban is a well-known anticoagulant medication that is used to prevent blood clots in patients with atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism. It is a direct oral anticoagulant that works by inhibiting the activity of Factor Xa, a key component in the blood clotting cascade. Apixaban has gained widespread acceptance due to its efficacy, safety, and ease of use. As a result, the demand for apixaban has been steadily increasing, leading to the emergence of several apixaban API manufacturers.
Apixaban API manufacturers are companies that specialize in producing the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) used in apixaban medications. These manufacturers are responsible for ensuring the quality, purity, and potency of the API, which is a critical component of the medication. Apixaban API manufacturers use advanced technologies and processes to produce high-quality APIs that meet regulatory standards.
There are several apixaban API manufacturers around the world, including large pharmaceutical companies and smaller specialty manufacturers. Some of the notable apixaban API manufacturers include Aarti Pharmalabs Limited (APL), Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Jubilant Life Sciences, and Hetero Labs. These companies have extensive experience in the pharmaceutical industry and have invested heavily in research and development to produce high-quality apixaban APIs.
Aarti Pharmalabs Ltd specializes in the clinical phase and commercial production of APIs and NCEs, intermediates, regulatory starting materials, key building blocks and xanthine derivatives. The company has a strong focus on research and development and has invested heavily in developing advanced technologies and processes to produce high-quality APIs. Aarti Pharmalabs has a strong presence in the Indian pharmaceutical market and has been expanding its operations to other regions.
Pfizer is a leading apixaban API manufacturer that produces the API under the brand name Eliquis. Pfizer has a strong presence in the pharmaceutical industry and has a proven track record of producing high-quality medications. The company has invested heavily in research and development to produce advanced technologies that enhance the quality and efficacy of its medications.
Bristol Myers Squibb is another major apixaban API manufacturer that produces the API under the brand name Eliquis. The company has extensive experience in the pharmaceutical industry and has a strong commitment to quality and safety. Bristol Myers Squibb has established itself as a reliable supplier of apixaban APIs to several pharmaceutical companies around the world.
The demand for apixaban APIs is expected to increase in the coming years, driven by the growing prevalence of atrial fibrillation and deep vein thrombosis. Apixaban API manufacturers will play a critical role in meeting this demand by producing high-quality APIs that meet regulatory standards. These manufacturers will need to invest in research and development to produce advanced technologies and processes that enhance the quality and efficacy of their APIs.
In conclusion, apixaban API manufacturers play a critical role in the production of apixaban medications. These manufacturers are responsible for producing high-quality APIs that meet regulatory standards and ensure the safety and efficacy of the medication. There are several notable apixaban API manufacturers around the world, including Aarti Pharmalabs Limited (APL), Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Jubilant Life Sciences, and Hetero Labs. These companies have extensive experience in the pharmaceutical industry and have invested heavily in research and development to produce high-quality apixaban APIs. The demand for apixaban APIs is expected to increase in the coming years, driven by the growing prevalence of atrial fibrillation and deep vein thromb.
0 notes
Photo

Apis and Intermediates Manufacturing Company in China
If you are looking for Apis and Intermediates Manufacturing Company in China then Jiwan Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd can be the best option for you. Where you can get many kinds of intermediates at affordable prices.
#10-Deacetylbaccatin III Suppliers Manufacturers#Apixaban Intermediates#Pharmaceutical Companies in China
0 notes
Text
Rivaroxaban Definition usage And advantages :
Rivaroxaban is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs). These drugs are used to prevent blood clots in people who are at risk of developing them. Rivaroxaban works by inhibiting the activity of certain enzymes in the blood, which helps to prevent the formation of clots.
One of the main uses of rivaroxaban (rivaroxaban API manufacturers in India ) is to prevent venous thromboembolism (VTE), a condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a vein, usually in the legs. VTE can be life-threatening if the clot breaks loose and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism (PE). Rivaroxaban can be used to reduce the risk of VTE in people who have undergone hip or knee replacement surgery, as well as in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF), a type of irregular heartbeat that increases the risk of stroke.
Rivaroxaban is also used to treat deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and PE in patients who have been diagnosed with these conditions. In these cases, rivaroxaban helps to prevent the clot from growing larger and reduces the risk of the clot breaking loose and traveling to the lungs.
One of the major advantages of rivaroxaban is that it is taken orally, which means that it does not require regular injections or infusions. This makes it a more convenient option for many patients. Another advantage of rivaroxaban is that it has a rapid onset of action, which means that it starts working within a few hours of being taken. In addition, the drug has a predictable anticoagulant effect, which makes it easier to manage and adjust the dose as needed.
Rivaroxaban is generally well-tolerated and has a good safety profile. However, like all medications, it can have some side effects. The most common side effects of rivaroxaban include bleeding, anemia, and nausea. In rare cases, rivaroxaban can also cause more serious side effects, such as severe bleeding or an allergic reaction.
In conclusion, Rivaroxaban is a widely use oral anticoagulant and has proven to be effective in preventing and treating blood clots in many people. Its oral administration, rapid onset of action, predictable anticoagulant effect and its good safety profile, makes it a widely accepted medication. As with any medication, it is important to talk to your doctor about the potential benefits and risks of rivaroxaban, as well as any other medications that you may be taking.
Visit : apixaban intermediate manufacturers to knowmore !
0 notes
Text
Takotsubo Caused by Pulmonary Embolism
Abstract
Takotsubo is a transient acute coronary myocardial infarction due to a catecholaminergic discharge accounting for 1 in 36,000 adults after intense physical or psychological stress. Most often found in women over 50 years of age. Its association with pulmonary embolism is very rare.
With this in mind, we report the case of a 76-year-old female patient with poorly followed chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). She presented to the emergency department with acute respiratory distress and lipothymia. Clinical examination revealed hypoxia with SaPO2 at 86% in free air, blood pressure at 120/80mmHg, tachycardia at 112 beats/min. The electrocardiogram showed S1Q3, hyper-right axial deviation, complete right bundle branch block with fragmented QRS, positive AVR with a tachycardia of 125 beats/min. A thoracic angioscan was performed, showing a bilateral pulmonary embolism of segmental and sub-segmental level. Ultrasensitive troponins were highly elevated at 1530ng/l with transthoracic echocardiography showing signs of acute pulmonary heart disease associated with apical ballooning, very akinetic with hyperkinesia of the bases, LVEF 26% suggestive of takotsubo confirmed by coronary angiography coupled with ventriculography giving an amphora-like appearance with a healthy coronary. The patient was initially admitted to the intensive care unit and then to the hospital for an intermediate-high risk pulmonary embolism complicated by takotsubo. The etiological work-up of the pulmonary embolism was normal. She received apixaban, Ramipril and bisoprolol. The evolution was marked by a recovery of the bi ventricular function with an LVEF of 58% in 1 month.
Takotsubo was secondary to respiratory failure caused by pulmonary embolism through catecholaminergic discharge resulting in a redistribution of beta receptors in the myocardium.
Read More about this Article: https://juniperpublishers.com/jojcs/JOJCS.MS.ID.555846.php
Read More Juniper Publishers Google Scholar: https://scholar.google.com/citations?view_op=view_citation&hl=en&user=rp_7-igAAAAJ&cstart=20&pagesize=80&citation_for_view=rp_7-igAAAAJ:_FxGoFyzp5QC
#Juniper publishers google scholar#Juniper Publishers#dentistry#dental implants#cardio-thoracic surgery#Minimally invasive#neurology
0 notes
Text
Pulmonary Embolism (3rd Edition) - eBook
Check out https://duranbooks.net/shop/pulmonary-embolism-3rd-edition-ebook/
Pulmonary Embolism (3rd Edition) - eBook

A must have resource for clinicians and investigators interested in pulmonary embolism and deep venous thrombosis. Pulmonary embolism (PE) is the third most common acute cardiovascular disease after stroke and acute myocardial infarction. This fully updated Pulmonary Embolism 3rd edition (PDF) supplies the latest information on methods of diagnosis, epidemiology, preferred diagnostic pathways, new medications including the new anticoagulants, and new recommendations for prophylaxis and treatment of PE and its immediate cause, deep vein thrombosis.
Stein’s Pulmonary Embolism 3rd edition:
Written by an internationally recognized and respected expert in the field
Highly illustrated with numerous graphs and tables alongside clear concise textbook
Includes chapters addressing pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep venous thrombosis (DVT) in relation to diseases and disorders such as; stroke, chronic heart failure, diabetes, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and many more
Discusses the role the different tools offered in imaging for PE, including echocardiography, multidetector computed tomography (CT), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), ventilation-perfusion (V-Q) imaging, dual energy CT, and magnetic resonance angiography
Contains 29 new chapters and includes new content on epidemiology of deep venous thrombosis; use of the new anticoagulants (dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban) for DVT and PE; indications and results with thrombolytic therapy and with vena cava filters; and information and indications for invasive mechanical thrombectomy and thrombolysis
Reviews
“An excellent contribution to the relevant contemporary literature…. I enjoyed reading the ebook and recommend it to my colleagues.��� World Journal of Surgery
“This textbook is cohesive, tightly organized, and has no repetition…. It is beautifully illustrated…and is my ‘go to’ source for rapid reference.” Journal of Interventional Cardiology
“I would recommend this ebook, Pulmonary Embolism 3e to all physicians looking after patients with venous thromboembolism … .The single author style has the advantage of a consistent format and lack of repetition, and the ebook is very well written.” Cardiology News
“Paul Stein … has used his vast knowledge and perspective to organize this definitive text … .In this long-awaited second edition he builds on the knowledge base regarding this common and yet often misdiagnosed condition. This text fills a gap in the knowledge-base of the physician, nurse, or therapist who cares for patients with pulmonary embolism. By using a clear and organized format with many graphs and diagrams, Stein provides detailed information beyond the scope of an online review, but in a readily searchable and easily accessible format. Stein does a nice job of explaining the challenges of using intermediate end points in the assessment of efficacy. Stein is clearly one of the world’s experts, and this far-reaching volume is a pleasure to read.” Respiratory Care
0 notes
Text
Eliquis Useful In Preventing Blood Clots, But Side Effects Include Major Bleeding Risks: Study
The controverisal new-generation blood thinner Eliquis does reduce the risk of venous thromboembolism among cancer patients, according to the findings of a recent study, but it also places patients at an increased risk of serious and potentially life-threatening bleeding problems.
In findings published earlier this month in the New England Journal of Medicine, Canadian researchers report that giving Eliquis to cancer patients cut the risk of certain types of potentially blood clots by more than half, but major bleeding events occurred in twice as many individuals given a placebo.
Researchers conducted a controlled, double-blind clinical trial on the efficacy and safety of Eliquis (apixaban), which is a member of a new-class of anticoagulants known as Factor Xa inhibitors, which also include Pradaxa and Xarelto. In the study, Eliquis was evaluated as a preventative measure for venous thromboembolism among ambulatory cancer patients with an intermediate to high risk of blood clots undergoing chemotherapy.
The study involved 563 patients in a modified intention-to-treat analysis, 288 of whom were given Eliquis and 275 of whom were given a placebo.
According to the findings, 12 of the 288 patients, or 4.2% given Eliquis suffered a venous thromboembolism. That compares to 28 of the 275 patients, or 10.2%, given a placebo. However, major bleeding events occurred in 10 of the Eliquis patients, compared to only five patients in the placebo group.
“Apixaban therapy resulted in a significantly lower rate of venous thromboembolism than did placebo among intermediate-to-high-risk ambulatory patients with cancer who were starting chemotherapy,” the researchers concluded. “The rate of major bleeding episodes was higher with apixaban than with placebo.”
Eliquis Bleeding Risks
Since the new-generation drugs have hit the market in recent years as a replacement for the older anticoagulation treatment warfarin, reports of severe and fatal bleeding problems with Eliquis, Xarelto and Pradaxa have surfaced nationwide. In many cases, the events were linked to a lack of an effective antidote to reverse the blood thinning effects of the drug, leaving doctors unable to control or stop bleeds.
Thousands of Eliquis lawsuits, Xarelto lawsuits and Pradaxa lawsuits have been filed in recent years, each raising similar allegations that the manufacturers failed to adequately warn about the bleeding risks and lack of a reversal agent.
Pradaxa was the first member of the class to hit the market, and the manufacturer previously agreed to pay more than $650 million in Pradaxa settlements in 2014, which resolved about 4,000 cases.
Bayer and Johnson & Johnson are currently facing more than 20,000 lawsuits raising similar allegations over the bleeding risks with Xarelto, which has become the most widely used member of the class. A handful of cases have gone to trial with mixed results, and the drug makers continue to maintain that it will defend individual claims and has refused to negotiate a settlement of the litigation.
In contrast, Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer have largely escaped liability for failure to warn about the side effects of Eliquis, after a federal judge appointed to preside over the litigation granted the drug makers motion to dismiss lawsuits early in the litigation.
The post Eliquis Useful In Preventing Blood Clots, But Side Effects Include Major Bleeding Risks: Study appeared first on AboutLawsuits.com.
0 notes
Photo

IPTG ( Isopropyl-Beta-D-Thiogalactoside)
Are you looking for a pharmaceutical company in China to supply high-quality Intermediates? Jiwan Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. is one of the most popular company in China. If you are looking for IPTG ( Isopropyl-Beta-D-Thiogalactoside) then you can contact us at +86-53155519016.
#Tedizolid API and Intermediates#Apixaban Intermediates#Pharmaceutical Companies in China#Anti-Cancer Intermediates China
0 notes
Text
Purchase IPTG from Jiwan Pharmtech

IPTG | 367-93-1 | Isopropyl-Beta-D-Thiogalactoside |Jiwan is a compound which is used in labs for the purpose of research. The compound is a mimic of lactose and its task is to activate lac operon for downstream gene transcription.
Afatinib(BIBW2992) API and Intermediates is a drug that is used to treat certain types of lung cancer. It belongs to the kinase inhibitors drug and has the task of stopping the growth of cancer cells. The tablet has to, be taken orally as per the prescription is given by the doctor.
Both these drugs can be purchased from Jiwan Pharmtech as the company sells them at a reasonable rate.
0 notes
Text
Contact Jiwan Pharmtech, Apis and Intermediates Suppliers

Jiwan Pharmatech is one of the Manufacturers China that manufactures many drugs for medicinal and experimental purposes. The company is one of the popular Pharmaceutical Companies In China and people can contact it for different types of medicine. Many Apis and Intermediates Suppliers are also available in China and this company is also one of the Apis and Intermediates Suppliers that provides the APIs for adding them to pain killers. The APIs produced by the company are approved by US FDA. The API is the main ingredient of painkillers, which relieve the patients from different types of pains.
#Apixaban Intermediates#DTT | Dithiothreitol | CAS 3483-12-3#Palbociclib and Intermediates#Docetaxel Manufacturers China
0 notes
Link
Jiwan Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd. provides the DTT | Dithiothreitol | CAS 3483-12-3, Palbociclib and Intermediates, Tedizolid API and Intermediates, Afatinib(BIBW2992)API and Intermediates at best prices in China. To know more, visit jiwanchem.com today!
#IPTG | CAS NO.367-93-1| Biochemicals | Jiwan#apixaban intermediates#Anti-Cancer Intermediates China
0 notes
Text
Juniper Publishers-Open Access Journal of Case Studies
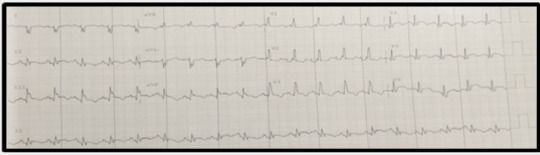
Takotsubo Caused by Pulmonary Embolism
Authored by N Mahoungou Mackonia
Abstract
Takotsubo is a transient acute coronary myocardial infarction due to a catecholaminergic discharge accounting for 1 in 36,000 adults after intense physical or psychological stress. Most often found in women over 50 years of age. Its association with pulmonary embolism is very rare.
With this in mind, we report the case of a 76-year-old female patient with poorly followed chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). She presented to the emergency department with acute respiratory distress and lipothymia. Clinical examination revealed hypoxia with SaPO2 at 86% in free air, blood pressure at 120/80mmHg, tachycardia at 112 beats/min. The electrocardiogram showed S1Q3, hyper-right axial deviation, complete right bundle branch block with fragmented QRS, positive AVR with a tachycardia of 125 beats/min. A thoracic angioscan was performed, showing a bilateral pulmonary embolism of segmental and sub-segmental level. Ultrasensitive troponins were highly elevated at 1530ng/l with transthoracic echocardiography showing signs of acute pulmonary heart disease associated with apical ballooning, very akinetic with hyperkinesia of the bases, LVEF 26% suggestive of takotsubo confirmed by coronary angiography coupled with ventriculography giving an amphora-like appearance with a healthy coronary. The patient was initially admitted to the intensive care unit and then to the hospital for an intermediate-high risk pulmonary embolism complicated by takotsubo. The etiological work-up of the pulmonary embolism was normal. She received apixaban, Ramipril and bisoprolol. The evolution was marked by a recovery of the bi ventricular function with an LVEF of 58% in 1 month.
Takotsubo was secondary to respiratory failure caused by pulmonary embolism through catecholaminergic discharge resulting in a redistribution of beta receptors in the myocardium.
Keywords: Pulmonary embolism; takotsubo cardiomyopathy; Myocardial infarction
Abbreviations: COPD: Followed Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease; APH: Acute Pulmonary Heart Disease; CICU: Cardiovascular Intensive Care Unit; LVEF: Left Ventricle; HPA: Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal; MI: Myocardial Infarction; CPA: Acute Pulmonary Heart; ARBs: Angiotensin 2 Receptor Blockers
Introduction
First described in a Japanese medical journal in 1990 about 5 cases, by the team of Hikaru Sato et al. [1-3] Takotsubo cardiomyopathy usually presents as transient left ventricular dysfunction with apical wall motion abnormalities associated with electrocardiographic changes similar to those of acute coronary syndrome in the absence of significant coronary disease [4,5]. It usually lasts about 15 days, without mortality or severity in the acute phase, and usually occurs in postmenopausal women, with 90% of cases in women aged 67-70 years [5], accounting for about 80% of cases in women over 50 years [4]. Takotsubo syndrome accounts for approximately 1-3% of all patients worldwide, or 1 case per 36,000 adults. In the USA, it accounts for 0.02% of hospital admissions and 1-2% of coronary syndromes in FRANCE [4,6]. The pathophysiological mechanism of takotsubo cardiomyopathy remains unclear, and several possible theories have been put forward, such as excess catecholamines, coronary artery spasm, microvascular dysfunction and metabolic disorders [3]. However, many of these theories focus on the central role of the sympathetic nervous system which, in response to an emotional, physical or combined trigger, releases an excess of catecholamines that cause the disturbance in myocardial kinetics. The mechanism by which catecholamines cause these contraction abnormalities is currently unclear [1], let alone its relationship to pulmonary embolism or being triggered by it. It is with this in mind that we report a case of pulmonary embolism causing takotsubo.
Case Report
We report the case of a 76-year-old female patient with poorly monitored COPD. She presented to the emergency department with acute respiratory distress and lipothymia. The clinical examination revealed hypoxia with SaPO2 at 86% in the open air and 97% under oxygen at 6litre/minute, blood pressure at 120/80mmHg, tachycardia at 112 beats/min. The electrocardiogram showed S1Q3, hyper-right axial deviation, complete right bundle branch block with fragmented QRS, positive AVR with a tachycardia of 125 beats/min. A thoracic angioscan was performed, showing bilateral segmental and sub-segmental pulmonary embolism. Ultrasensitive troponins were highly elevated at 1530ng/l with transthoracic echocardiography showing signs of acute pulmonary heart disease (APH) associated with apical ballooning, very akinetic with hyperkinesia of the bases, LVEF 26% suggestive of takotsubo confirmed by coronary angiography coupled with ventriculography giving an amphora-like appearance with a healthy coronary. The patient was initially admitted to the Cardiovascular Intensive Care Unit (CICU) and then to the hospital for an intermediate-high risk pulmonary embolism complicated by takotsubo. The etiological work-up of the pulmonary embolism was normal. She initially received oxygen therapy for 72 days, apixaban (Eliquis) 10mg x2/dr for 7 days then 5mg x2/dr for 6 months. Ramipril 5mg/dr, bisoprolol 2.5mg/dr. The evolution was marked by a recovery of the biventricular function at 1 month of the treatment with a LVEF at 45% in 2 weeks then at 58% in 1 month.
Discussion
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy is a transient stress cardiomyopathy, the symptomatology of which is highly suggestive of acute myocardial infarction [2]. It usually occurs in postmenopausal women and accounts for about 90% of women with a mean age of 67-70 years. A woman over 55 years of age is 5 times more likely to develop takotsubo than a younger woman, and 10 times more likely than a man [1,2]. Several factors are incriminated in the occurrence of takotsubo. Among them we have :
a) Contributing factors:
i. Falling blood levels of estradiol at the menopause (estradiol seems to protect the microcirculation from the vasoconstrictive effect of adrenaline);
ii. Genetic predisposition, supported by the existence of family cases;
iii. A history of psychiatric illness observed in 42% of cases (e.g. depression in 20% of cases, anxiety) or neurological illness.
b) Triggering factors:
i. Physical stress (stroke or TIA, subarachnoid haemorrhage, acute respiratory failure, accident, strenuous sports activity, cancer chemotherapy, even coronary disorders).
ii. Negative psychological stress (bereavement, divorce, anger, anxiety, financial or professional problems, floods, earthquakes, etc.), but also positive (happy surprises) [2].
Studies that have investigated the pathophysiology of Takotsubo syndrome highlight the central role of strong sympathetic stimulation and parasympathetic depression [2]. Indeed, there are two initial elements of physiology to consider. The first is the cognitive centres of the brain and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, and the amount of epinephrine and norepinephrine released in response to a given stress (i.e. the "gain" of the HPA axis). The second is the response of the cardiovascular system (including the myocardium, coronary arteries and peripheral vasculature) and the sympathetic nervous system to sudden sympathetic activation and the surge in circulating catecholamines. Serum catecholamine levels at presentation are significantly higher than resting levels in the same patient or in comparable patients with acute heart failure due to acute myocardial infarction (MI), suggesting a potential for excessive HPA gain and epinephrine release. However, there is currently no proven pathophysiological mechanism to clearly explain Takotsubo syndrome. There may be a synergistic combination of more than one factor, and mechanistic studies have produced conflicting results [7]. The main manifestation of takotsubo is an acute coronary syndrome characterised by angina, repolarisation disorders on the electrocardiogram with, in particular, the pathognomonic sign of an AVR lead with positive T waves, combined with the absence of negative T waves in the V1 lead [3,4]. Elevated cardiac biomarkers and kinetic disturbances are associated with severe left ventricular dysfunction such as transient akinesia or dyskinesia of the apical segments, resulting in ballooning and base preservation [1,2,8,9]. Coronary angiography usually finds healthy coronary arteries in 70-90% of cases, with ventriculography usually showing a characteristic amphora pattern and left ventricular wall motion abnormalities [2]. Early cardiac MRI shows global kinetic disturbances in the apical and medial segments with edematous T2 hypersignal of the apex and middle part of the left ventricle without late enhancement or perfusion abnormalities suggestive of myocarditis or infarction [10].
Pulmonary embolism is a serious and fatal condition, representing the third leading cause of death worldwide after cardiovascular disease and cancer, according to the French Federation of Cardiology in 2021 [11]. Its association with takotsubo is unclear, but increased catecholamine levels during severe pain or respiratory distress associated with pulmonary perfusion defects related to pulmonary embolism appear to lead to the development of left ventricular wall motion abnormalities [12].
Our patient is a 76 year old woman, menopausal, presenting with physical stress such as respiratory distress which constitute three factors favouring takotsubo. The diagnosis in our case was oriented by an electrocardiogram which showed a positive AVR lead although we noted an S1Q3 aspect, a hyper-right axial deviation with a complete right bundle branch block associated with repolarization disorders with fragmented QRS in favour of a pulmonary embolism. Biological markers were strongly positive and rarely encountered in pulmonary embolism. On transthoracic echocardiography, apart from the signs of CPA, we noted severe dysfunction of the left ventricle involving the apical and medial segments with apical ballooning and conservation of the bases, with diagnostic confirmation on coronary angiography coupled with ventriculography as reported in the literature, which objectified healthy coronaries with an amphoric aspect of the left ventricle. Pulmonary embolism in us being at high risk, seems to be at the origin of takotsubo, given the extent of the pulmonary artery involvement and the severity, causing respiratory failure that may be at the origin of a catecholaminergic storm. This causes a redistribution of myocardial beta receptors with a predominance of Gs forms (negative inotropes) at the apex, while G1 type beta receptors (positive inotropes) remain dense at the base. This mechanism is responsible for a dysfunction of the left ventricle with an aspect of apical ballooning in systole causing a decrease in coronary perfusion by a phenomenon of microvascular spasm, responsible for direct lesions of the myocytes as well as a metabolic disorder in the myocardium [13].
The treatment of takotsubo is mainly based on the use of ACE inhibitors and angiotensin 2 receptor blockers (ARBs) as an improvement in one-year survival has been observed with a decrease in recurrence. Whereas bêta-blockers, proposed in the therapeutic strategy, do not seem to be effective in the long term with a recurrence rate of 30%. Antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants are used on a case-by-case basis in combination with treatment of the cause [1,5]. In our case, patient was treated with Ramipril, bisoprolol for takotsubo and apixaban for pulmonary embolism.
Conclusion
Pulmonary embolism associated with takotsubo cardiomyopathy is rarely described to date given its mechanism of occurrence and the severity of the two pathologies that can cause sudden death. This second entity is rarely encountered and sometimes unrecognised, and may have a poor immediate vital prognosis with rapid recovery.
To know more about Juniper Publishers please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/manuscript-guidelines.php
For more articles in Open Access Journal of Case Studies please click on: https://juniperpublishers.com/jojcs/index.php
#JuniperPublishers#juniper publishers contact info#Emergency Medicine#Medical Genetics#Obstetrics and Gynaecology#Otolaryngology#Physiology
0 notes
Link
Jiwan Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd that provides pharmaceutical API and Intermediate with high-quality. Here you can get different types of intermediates like such as apixaban intermediates, docetaxel intermediates, and tedizolid API, etc. If you are searching for Vildagliptin and Intermediates supplier in China, then you can contact us at +86-53155519016.
#DL-Dithiothreitol Supplier | CAS 3483-12-3#Tedizolid API and Intermediates#Anti-Cancer Intermediates China
0 notes
Link
Jiwan Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd is one of the most popular pharmaceutical company in China. We are manufacturing and supplying all kinds of pharmaceutical chemicals like - Cabozantinib and Intermediates, Apixaban Intermediates, and Palbociclib and Intermediates, etc. with better quality and affordable price.
0 notes